Corrections and Updates
Last revised 2012 August 19
This page will be revised as the need arises. Note however that it is not possible
to track every change in the digital camera industry, and you should always use the World Wide Web
and other current sources of information to help you make decisions.
New technology:
See my New DSLR Notes page for extensive updates.
Red sensitivity: I have reliable reports that the Pentax K-r and K-x have considerably
more deep-red sensitivity than competing Canon and Nikon DSLRs. I have not yet evaluated them for
astrophotography in detail.
Known misprints in the first printing:
The pictures on pages 176, 179,
186, and 189 were printed with insufficient contrast.
Page 186 is the worst afflicted. To see these pictures properly
on your computer screen, view the
sample pages.
[p. 212]
| Change: |
|
DSLR Focus 95, 95 |
| To: |
|
DSLR Focus, 95 |
Other clarifications for the second printing:
[p. 6, footnote]
| Change: |
|
On the Web at http://web.canon.jp/Imaging/astro/index-e.html. |
| To: |
|
Formerly on the Web at http://web.canon.jp/Imaging/astro/index-e.html. |
Canon took this web site down in early 2008, apparently feeling that it was no longer up to date.
[p. 50]
| Change: |
|
Recently, Meade Instruments introduced
a design they call Ritchey-Chrétien...
|
| To: |
|
In 2005, Meade Instruments introduced
a design they called Advanced Ritchey-Chrétien...
|
| |
| Change: |
|
However, the decision to call it
Ritchey-Chrétien is controversial, and the name may not stick.
|
| To: |
|
The decision to call it Ritchey-Chrétien
was controversial, and in 2008 Meade agreed to stop using that name.
|
In fact, the change came in response to a lawsuit. For now, the illustration at the top of p. 50 is
not being changed because these telescopes are already in users' hands and were bought as a type of
Ritchey-Chrétien. Meade's optical system is a good one; it just isn't a Ritchey-Chrétien.
[p. 78, caption]
| Change: |
|
decentered element |
| To: |
|
decentered element or misaligned T-ring |
If the lens is attached with a T-ring (as some older lenses are), misalignment
(non-perpendicularity to the sensor plane) can arise there.
To fix a misaligned T-ring, loosen and retighten the screws that
hold the inner part of the T-ring in place
relative to the outer part.
[p. 95]
| Change: |
|
best known and most elaborate is |
| To: |
|
first to achieve wide use was |
| Change: |
|
which has gradually evolved |
| To: |
|
which gradually evolved |
Updates to DSLR Focus seem to have stopped in 2006,
but I have seen no actual announcement of discontinuation.
Other focusing software is being updated regularly to support newer cameras.
[p. 171]
| Change: |
|
because 0.51/2.2 = 0.73 |
| To: |
|
because 0.5 = 0.732.2
|
in order to more closely match the preceding formula.
The text is correct, but the original example caused some confusion.
[p. 179, figure caption]
| Change: |
|
Left: ... Right: |
| To: |
|
Top: ... Bottom: |
[p. 187]
The illustration on p. 187 does not make clear why the boxcar filter is used.
Here's a revised version with a better explanation:
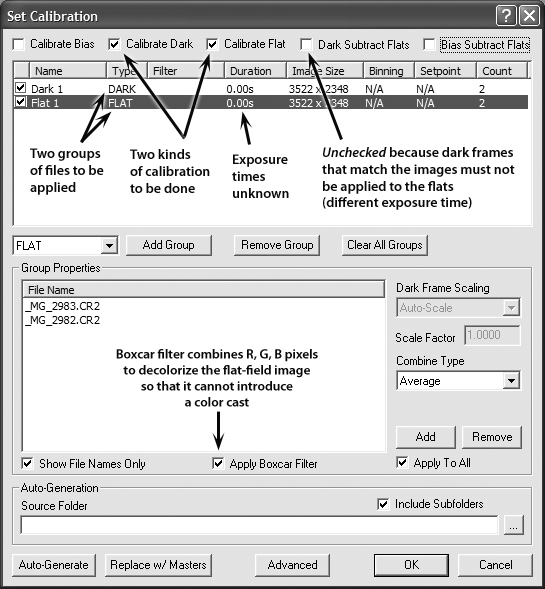
Click here to download EPS version
More importantly, regarding flat-fielding, see the correction below.
Other notes
Important correction: The book gives a procedure for flat-fielding that does not include
flat darks or bias frames. That is wrong. Contrary to what I thought at the time,
DSLRs have appreciable bias (that is, their pixel values do not start out at 0).
Accordingly, flat fields should be accompanied by matching dark frames ("flat darks")
for the sake of bias correction even though the exposures of flat fields are so short
that dark frames are not needed for the sake of noise.
Be sure to use many calibration frames — numerous darks and flats — for the same
reason that you take numerous exposures of the celestial object: to keep down the grain.
It makes no sense to take 10 exposures of a celestial object (to avoid grain) and then
do the calibration with just one dark or flat frame (thereby reintroducing a lot of grain).
|